
The Ultimate Guide to Understanding Market Trends and Price Action
 ACY Securities - Jasper Osita
ACY Securities - Jasper Osita
Welcome to our deep dive into Market Trends and Price Action, the blueprint of price movement that lays the foundation for every successful trading strategy.
In this blog, we'll explore how market structure represents the very framework of price swings, market trends, support and resistance levels, and distinct market phases, all of which come together to tell the story of where the market has been and where it might be headed.
In the sections that follow, we'll break down:
- What is a Market Structure?
How it represents the dynamics of price movement.
- The Importance of Market Structures:
Mastering this concept is key to interpreting market sentiment and making informed trading decisions.
- Identifying Swings and Trends:
Using patterns like Higher Highs, Lower Lows, and more to gauge market direction.
- Drawing Support and Resistance Levels:
How these levels serve as the critical points for trade entries and exits.
- Market Phases – AMD
A look at accumulation, manipulation, and distribution to reveal the narrative behind price movements.
By applying these concepts to your trading routine, you'll learn to map out the market’s structure, anticipate potential moves, and ride trends with confidence while effectively managing risk.
What is a Market Structure?
Imagine looking at a chart of EUR/USD or a stock like AAPL. Each peak and trough, each rejection at a support or resistance level, is a piece of the puzzle. When you see a series of higher highs and higher lows, it tells you that buyers are in control, signaling an uptrend. Conversely, lower highs and lower lows indicate a downtrend. And when prices settle into equal highs and lows, the market is likely range-bound, moving sideways without a clear direction.

Market structure represents the framework of price movement, including swings, support/resistance, and phases.
Understanding these elements isn’t just academic—it’s practical. Recognizing market phases like Accumulation, Manipulation, and Distribution enables you to identify when the market is quietly building positions, when it’s gearing up for a breakout, and when it's time to take profits before a reversal occurs.
Importance of Market Structures
A solid grasp of market structure allows you to make informed decisions, interpret market sentiment, and set up reliable trade entries and exits. It’s the foundation upon which all trading strategies are built.
- Serves as the foundation for making informed trading decisions.
- Help traders interpret potential market direction based on price formations.
- Essential for developing reliable entry and exit strategies.
Applying Market Structure to Your Trading
Market structure represents the blueprint of how prices move over time, and mastering it is the foundation for all trading strategies. By recognizing key patterns—such as swings, support and resistance levels, and the phases of market behavior, you can better gauge where the market is heading and make more informed trading decisions.
Imagine you’re looking at a chart of EUR/USD or a stock like $AAPL. The chart is filled with peaks and troughs that tell a story:
2 Types of Market Structures

- Trending Market:
A trending market shows clear directional movement, which can be easier to trade as the trend provides guidance on potential entries and exits.
- Non-Trending (Range-Bound) Market:
In a range-bound market, prices oscillate between fixed levels. Recognizing these conditions is key to applying breakout or reversal strategies effectively.
Identifying Swings and Trends
To further understand the market structure, we also need to understand how it is being built. As mentioned above, a market structure comprises of a combination of market swings, swings highs and swing lows.

When you see a series of higher highs (HHs) and higher lows (HLs), you know buyers are in control, and the market is in an uptrend. Conversely, lower highs (LHs) and lower lows (LLs) indicate a downtrend. In a sideways or range-bound market, equal highs (EHs) and equal lows (ELs) are obvious, suggesting no clear direction.
Key Concepts:
- Higher Highs (HHs) & Higher Lows (HLs): Uptrend Price Action
- In an uptrend, the market consistently creates new highs and retraces and creates higher lows. This pattern signals that buyers are in control.
- Lower Highs (LHs) & Lower Lows (LLs): Downtrend Price Action
- Conversely, a downtrend is marked by lower highs and lower lows, indicating sellers dominate the market.
- Equal Highs (EHs) & Equal Lows (ELs): Sideways Price Action
- If price is neither on an obvious trending condition, whether up or down, probably it’s on range-bound or sideways market.
Support and Resistance
These are the levels where price has historically struggled to move past. Support acts as a floor when prices decline, and resistance serves as a ceiling when prices rise. By drawing these levels, you can pinpoint potential entry and exit points. For instance, once you identify that the price has been rejected at a specific resistance level several times, you might prepare for a breakout when that level is finally surpassed.
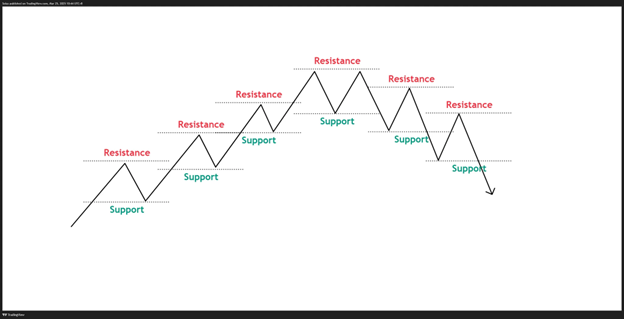
Swings cannot be created if there are no support or resistance levels being created.
- We consider Swing High after the price hitting a Resistance, preventing it for an upside move.
- We consider a Swing Low after price hitting a Support, preventing it for a downside move.
Drawing Support and Resistance Levels

Step 1: Identify an Initial Move.
Step 2: Wait for price to reject.
Step 3: Wait for the price to find support.
Step 4: Wait for a breakout.

Market Phases – AMD (Accumulation, Markup, Distribution)
A market structure has phases. It’s not enough to follow price without understanding the narrative or the story behind its price movements.

When examining the market behavior, you can see a classic example of the three primary market phases:
- Accumulation:
This is the phase where liquidity is being pooled as the market is going on sideways.
During the Accumulation phase, the market trades in a narrow range as buyers quietly build positions.
- Manipulation:
In the Manipulation phase, the market is engineered taking out either side of the market before going to the actual direction. Knowing the manipulation phase keeps you out of the market and waiting for the coast to be clear before you look for opportunities.
During the manipulation phase, price stages a breakout but pulls back inside the range, taking out the weak hands. Another scenario are price break down on the opposite side then quickly reverses to the upside, taking out stop loss orders on both sides.
- Distribution:
Finally, in the Distribution phase, as the manipulation is already done, and the needed liquidity has already been gathered, this is where we’d want to ride where the price is now ready to go in a certain direction.
This is the phase after the manipulation, or the liquidity has already been taken out and its ready to go to the actual direction.

Once we understand how market structure works, how to plot levels, and its phases, the next step is to identify where price is going.
Understanding market structure is the essential first step—it equips you with the knowledge of how prices behave and forms trends.
How to Apply Market Structure Analysis in Your Trading
- Identify the Current Market Type:
- Trending Market: Look for clear patterns of HHs/HLs (uptrend) or LHs/LLs (downtrend).
- Range-Bound Market: Observe if price oscillates between equal highs and lows, indicating sideways movement.

In this case, the price previously was on a downtrend market and paused by creating a sideways market.
Currently, the price has already broken out of the range with a potential to go for another upside move.
Based on the structure, we are on an uptrend market coming from a sideways market and downtrend market.
2. Mark Support and Resistance Levels:
- Step 1: Identify the initial move where price begins its directional shift.
- Step 2: Wait for the price to be rejected at a potential resistance (or support) level.
- Step 3: Confirm that price has found support (or encountered resistance) by observing multiple touches on the level.
- Step 4: Look for a breakout from these levels as confirmation of the next move.
3. Determine the Market Phases:
- Accumulation: Identify when the market is quiet and range-bound; this is where smart money builds positions.

Wait for price to reveal its intent by waiting for price to break out or breakdown.
- Manipulation: Wait for price to trigger a breakout or breakdown at the resistance or support levels. Observe price on the lower timeframe if it is creating
Price, if institutions are present, will stage a breakout that could be a fake out.

Price trade to break out but it did not close above the range, signaling a potential fake out.
We can check a much lower timeframe to confirm if it’s going to breakout or breakdown.

Going on the M5 Timeframe, we can see that price failed to break out and proceed to breakdown on the lower timeframe, signaling a reversal move.
2 Trade Approaches:
- Reversal Trade

- We are currently on an uptrend market, but it seems that price failed to breakout successfully, we can look for a potential breakdown on the lower timeframes. Which in this case, we had a breakdown on M5 Timeframe for downside potential.
- You can trade the breakdown by entering short at the support level once its
- Target for this is just the next low since overall, we are still on an uptrend market.
2. Manipulation Trade
- Wait for price to go on the other end of the range and look for confirmations that it is now willing to go in its actual direction based on the higher timeframe.


- Once price reaches the other side go again at the lower timeframe to look for a breakout.


With this method, we can trade in favor of the trend.
- Distribution: Be alert to a slowdown in momentum or price reaching historical highs/lows; it might be time to lock in profits or prepare for a reversal.


Targets can be set at the previous resistance levels. You can also set targets at 2R to 3R.
If you are going to hold the position, be careful, as manipulations on previous lows can still occur along the way and could even proceed to a reversal.
By integrating these concepts into your trading routine, you can develop a more disciplined, informed approach that increases your chances of making the right moves in the market. This holistic view—from understanding market structure to executing precise trades—empowers you to ride trends confidently and manage risk effectively.
LiquidityFinder
LiquidityFinder was created to take the friction out of the process of sourcing Business to Business (B2B) liquidity; to become the central reference point for liquidity in OTC electronic markets, and the means to access them. Our mission is to provide streamlined modern solutions and share valuable insight and knowledge that benefit our users.
If you would like to contribute to our website or wish to contact us, please click here or you can email us directly at press@liquidityfinder.com.
